Melanotan 2 and Melanocortin Signaling
Melanotan 2 exerts its effects by interacting with various melanocortin receptors, which are part of a group of five distinct receptors, each serving different functions. Notably, MT-2 primarily binds to MC-4R and MC-1R, with a weaker affinity for MC-3R.
Here's a breakdown of the known functions of these melanocortin receptors:
- MC-1R: Found on melanocytes, the activation of MC-1R leads to the darkening of both the skin and hair.
- MC-2R: Located in the adrenal glands, MC-2R binding stimulates the secretion of adrenal hormones, including cortisol.
- MC-3R: Although its precise role is not fully understood, MC-3R appears to be involved in appetite control and energy regulation.
- MC-4R: Activation of MC-4R brings about changes in feeding patterns and sexual behavior. Additionally, it influences male erectile function and energy homeostasis.
- MC-5R: MC-5R is present on sweat glands and pancreatic islet cells, although further details about its functions are currently limited.
Melanotan 2 and Autism
The most recent research on MT-2 has uncovered promising findings, indicating that this peptide can potentially reverse certain autistic features in a widely used mouse model of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Currently, there is no specific treatment for ASD, but recent studies have suggested that oxytocin therapy might be helpful in mitigating some of the behavioral challenges associated with the condition. In this context, researchers utilized a mouse model of maternal immune activation known to result in autism and investigated whether MT2, known for stimulating oxytocin release, could counteract ASD or reduce typical ASD behaviors.
Their research unveiled significant results, showing that administration of MT-2 effectively reversed the decreased communication, impaired social interaction, and repetitive behaviors commonly associated with autism in this particular model. Interestingly, the researchers also observed that MT-2 administration led to an increase in the expression of oxytocin receptors in specific brain regions, implying a direct correlation between oxytocin signaling in those areas and the expression of ASD-specific behaviors[1]. These findings offer a promising avenue for further exploration and potential therapeutic interventions for ASD.
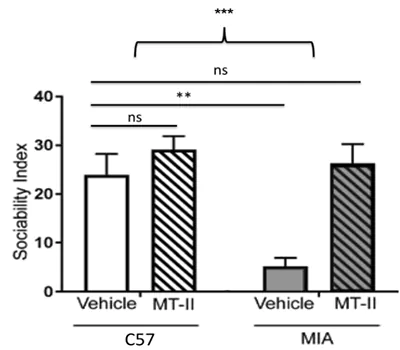
Impact of MT-2 on sociability in rats with ASD (MIA) showing that MT-2 returns sociability ratings to near the baseline of control animals (C57).
Source: PubMed
These findings not only suggest potential avenues for developing a treatment for ASD, they have helped to define a specific brain pathway that may be integral to the development of ASD in the first place. These findings could help scientists develop a complete model of ASD and thus both treatments and preventative measures.
Melanotan 2 and Hunger
There is compelling evidence indicating that MT-2 can effectively reduce fat storage and hunger behavior in animal models. Researchers have discovered that MT-2 acts as a potent agonist of the melanocortin-4 receptor (MC-4R), which plays a crucial role in food preferences and intake. Administering MT-2 to mice results in significant reductions in food consumption and alters their preference for fatty foods. Surprisingly, mice given MT-2 ignore fatty foods, which they would otherwise prefer. Conversely, mice lacking the MC-4R receptor show an exclusive preference for fatty foods and are unaffected by MT-2's effects[2].
The impact of MT-2 on satiety is akin to that of leptin, often referred to as the "satiety hormone" due to its ability to reduce cravings and food intake. However, leptin has not proven effective in treating obesity, even in individuals deficient in leptin. This discrepancy may be attributed to two distinct pathways for satiety, known as the leptin-dependent and leptin-independent pathways. Research suggests that MT-2 more effectively stimulates both pathways, making it a potentially more efficacious exogenous treatment for reducing hunger[3], [4]. This notion is further supported by the finding that MC-4R stimulation also affects the gene expression of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which is associated with the leptin-satiety pathway[5]. Both MT-2 and leptin are believed to increase TRH expression in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, a region of the brain linked to satiety and food intake. However, only MT-2 crosses into the central nervous system at concentrations high enough to impact TRH expression.
Melanotan 2 and Diabetes
The development of diabetes is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, excessive glucagon secretion, and the production of ketone bodies[6]. Over time, it has been established that leptin effectively counteracts these factors by promoting glucose uptake, inhibiting glucagon production, and interfering with the pathway that leads to ketone body formation. Importantly, these actions do not rely on insulin, making leptin signaling an intriguing alternative avenue for potential diabetes treatment.
Studies have demonstrated that leptin's impact on blood sugar is mediated through melanocortin receptors, and interestingly, MT-2 elicits similar effects[7]. This finding holds significance because leptin primarily exerts its effects in the brain but encounters difficulty crossing the blood-brain barrier as effectively as MT-2. Consequently, when leptin is administered exogenously, it does not reach the central nervous system (CNS) in significant quantities, diminishing its effectiveness as a drug and giving MT-2 an advantage. Despite both peptides having nearly identical effects on melanocortin receptors, MT-2's ability to more readily reach the CNS provides it with a valuable edge.
Melanotan 2, Impulse Control and Alcohol Intake
Building on the notion that MT-2 might influence oxytocin signaling and consequently impact behavior in ASD, research also indicates that the MC-4R receptor could be involved in impulse control. Previous studies in rats have demonstrated that MT-2 administration reduces alcohol intake and increases water intake, even in rats with a preference for alcohol[8]. More recent investigations have shown that melanotan-2 works synergistically with naltrexone, significantly enhancing its efficacy by more than seven-fold, effectively reducing binge-like ethanol intake in mice[9].
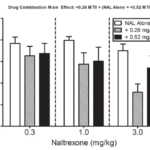
Percent of baseline alcohol consumption in mice treated with naltrexone or naltrexone and MT-2.
Source: PubMed
The discoveries indicate that MT-2 could serve as more than just a valuable treatment for alcohol-related disorders. Instead, the peptide seems to be influencing a fundamental mechanism of craving and desire within the mammalian brain. This research has the potential to unveil broader insights not only into alcohol abuse and hunger but also the involvement of oxytocin in impulsive behavior. Moreover, it might pave the way to identify craving pathways and enhance our comprehension of human motivation, impacting various aspects of life, from work to relationships.
Melanotan 2 and Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is frequently linked to vascular issues, and it can be successfully addressed in most men through medications like sildenafil (Viagra) and similar drugs that enhance blood flow by reducing vascular resistance. However, not all cases of ED are solely related to vascular problems, which renders sildenafil and similar drugs ineffective for a small percentage of men and the majority of women who suffer from hypoactive sexual desire disorder.
MT-2 has long been recognized as an effective treatment for ED, but research indicates that its impact extends beyond drugs like sildenafil, primarily due to its actions in the central nervous system. A study involving men who had previously failed to respond to Viagra revealed that eighty percent of them experienced positive results with MT-2 treatment[10]. Furthermore, MT-2 has been the subject of active investigation as a potential treatment for sexual desire disorders in both men and women.