Gonadorelin Research and Breast Cancer Prevention
Gonadorelin research has shown potential in breast cancer prevention through various mechanisms.
Raloxifene and antiestrogenic gonadorelin: A study published in Cancer Prevention Research found that both raloxifene and gonadorelin inhibit intestinal tumorigenesis by modulating immune cells and decreasing stem-like cells. This suggests a potential role for gonadorelin in cancer prevention.
Gonadorelin and micrometastatic breast cancer: According to a study published on PMC, gonadorelin can occupy the receptors for gonadorelin in the pituitary gland, potentially preventing the recurrence of micrometastatic breast cancer.
Targeted drug delivery for breast cancer: Functionalized liposomes have been studied as a delivery system for targeted breast cancer drug delivery. This approach shows promise in improving treatment strategies for breast cancer.
Hormone agonists for breast cancer prevention: Hormone agonists, such as gonadorelin and goserelin, have been explored as potential options for breast cancer prevention. Economic studies have evaluated the cost-effectiveness of these prevention strategies.
Ovarian ablation with gonadorelin analog: An article published in Nature discusses the proposal of temporary ovarian ablation using a gonadorelin analog as a preventive strategy for breast cancer. This study aims to determine the effects of risk factors and prevention strategies on breast cancer development.
Gonadorelin a Breakthrough in Prostate Cancer
New breakthroughs in the treatment of prostate cancer have emerged, including the use of Gonadorelin. This hormone therapy has shown promising results in lowering testosterone levels in certain patients with prostate cancer. By reducing testosterone levels, which is necessary for cancer cell growth, Gonadorelin may help slow down or even stop the progression of the disease.
According to a study published in the Journal of Urology, testosterone breakthrough rates during androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) for castration-sensitive prostate cancer were observed to be significantly reduced with the use of Gonadorelin. This indicates the potential effectiveness of Gonadorelin in suppressing testosterone levels and managing the disease.
The FDA has also approved the first oral hormone therapy for advanced prostate cancer, which further supports the potential benefits of hormone therapies like Gonadorelin in treating this condition. These hormone therapies, including ADT, aim to halt testosterone production or block its effects on prostate cancer cells.
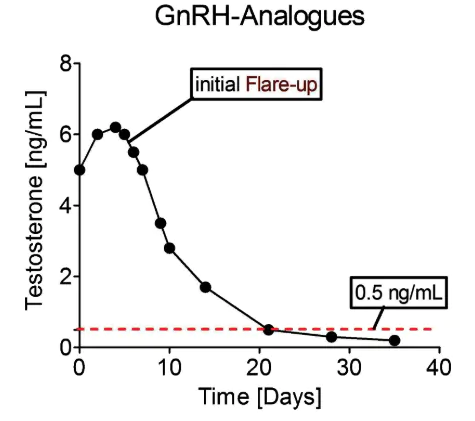
The impact of gonadorelin and GnRH analogues on testosterone levels
Source: PubMed
Gonadorelin May Reduce Dementia Risk
Recent studies have suggested that Gonadorelin, a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist, may play a role in reducing the risk of dementia. Dementia is a progressive neurological disorder characterized by a decline in cognitive function, memory loss, and impaired daily functioning. It affects millions of people worldwide, with Alzheimer's disease being the most common form.
One study published in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) found a potential link between the use of GnRH agonists and a reduced risk of dementia or Alzheimer's disease. The study compared different types of androgen deprivation therapy and their association with dementia risk. Interestingly, the use of antiandrogen monotherapy was associated with an increased risk of dementia or Alzheimer's disease. In contrast, GnRH agonist use and orchiectomy (surgical removal of the testicles) were not linked to an elevated risk.
Another review published in PMC explored alternative treatment options for Alzheimer's disease, including targeting the release of luteinizing hormone (LH), which GnRH regulates. The review suggested that targeting LH release through the use of GnRH agonists could be a successful strategy in preventing or delaying the progression of Alzheimer's disease.
Furthermore, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) has also been implicated in reducing the risk of dementia. A study mentioned by CNN found that taking hormone replacement therapy at the right time in midlife can reduce the risk of dementia and Alzheimer's disease by 23% to 32%.
While some studies suggest a potential protective effect of hormonal therapies like Gonadorelin and HRT on dementia risk, it is important to note that research findings on this topic have been inconclusive and contradictory at times. More research is needed to fully understand the relationship between these therapies and dementia risk.

